Berthing Ship Protection Inflatable Floating Rubber Yokohama Fender
Product Introduction
The basic body construction of rubber Yokohama fender consists of an outer layer made of rubber, cord layers and inner rubber layer vulcanised together. End flanges are available at both ends for air charging purposes. The outer rubber layer is made of strong rubber material to withstand external forces and protect the other layers from abrasion as well as hard usage on bad weather conditions. Cord layers are innovatively designed at ideal angles to evenly distribute the stress acting upon the fender. Overall winding technology and the cord layers with high tensile stress are applied to provide strength and hold the internal pressure during usage. This helps distribute the stress uniformly, maintaining the energy absorption and increasing its efficiency. The inner layer is tasked to seal the air inside, minimising the air leakage using a material with airtight qualities.
Advantage of Rubber Yokohama Fender
Advantages During Inclined Berthing
During berthing, the initial contact with the dock is usually at an oblique angle and that places a lot of pressure on both surfaces (the dock and the ship).
For typical solid rubber fenders, at inclined compression which is usually the case, energy absorption decreases considerably. Therefore, it is not unusual to see solid fenders used are larger in sizes. On the other hand, pneumatic fenders’ energy absorption maintains at a relatively high level despite inclined compression. Due to a more evenly distribution of load pressure, the torque performance against the dock is usually smaller when compared to conventionally designed solid fender systems.
Stronger Against Shearing Force
After making contact with the dock, the vessel is usually slowly moved to the optimum mooring position. This action exerts high shearing force and compression on the surface of fenders. Most solid fenders are severely damaged due to such forces as they are not designed to withstand strong shearing forces and friction that way. However, it depends on the designs/types of solid fenders. For example, MAX frontal pads for solid fenders are designed to tackle this issue and protect the fenders from shearing forces, in which the surface of fenders do not make contact with the ship.
Relatively Safe Even During Excess Load
Generally speaking, all fenders should be used within the impact load limit. However in real life situations, it is common to see that fenders often accidentally receive excess loads. When that happens, the fortunate thing about a pneumatic fender is that the reaction force does not increase sharply under excessive load. In contrast, solid fenders’ reaction forces tend to spike sharply under excessive load conditions and damage the ship during the mooring process. This is also helped by pneumatic type fenders’ characteristic that enables a more uniform distribution of stress.
Advantages During Crucial Weather Conditions
During crucial weather conditions when the wave action is severe, mooring processes are further complicated due to up and down unbalanced action at the quay. This exerts a higher shearing force on the fenders and the frequently change in forces during mooring under such weather conditions will cause fatigue on typical solid type fenders. However on the other hand, pneumatic fender’s flexible contact area and large allowable deflection characteristics minimise fatigue during such situations. In fact, for seas with rough situations or frequent bad weather conditions, pneumatic types may be a better option than solid type fenders as it may display a longer life span.
Deterioration in Performance Minimised
Aging and fatigue often cause fenders to deteriorate in terms of performance. However, due to its air filled body and highly elastic material, such issues are minimised. Solid rubber fenders or foam fenders depend more on the hardness of the material and such dependance may result in decrease in energy absorption performance after years of usage and temperature change. On the other hand, as long as basic maintenance and air pressure control is maintained, pneumatic fenders remain optimum performance even at extremely low temperature down to -50 Degree Celsius or even during high fluctuations.
Tide Adaptation
Pneumatic fenders are primarily floating-types, which means the fenders float on the water in an unrestricted vertical plane corresponding to the tidal range and ship’s vertical movement. Therefore, fender energy absorption always take place at the most optimum position.
Specificaton of Rubber Yokohama Fender
| Size |
Initial Internal Pressure 50kPa |
Initial Internal Pressure 50kPa |
|
Diameter/
Meter
|
Length
/Meter
|
Energy Absorption /KJ |
Reaction Force /KN |
Energy Absorption /KJ |
Reaction Force /KN |
| 0.5 |
1 |
6 |
64 |
8 |
85 |
| 0.7 |
1.5 |
17 |
137 |
24 |
180 |
| 1.0 |
1.5 |
32 |
182 |
45 |
239 |
| 1.0 |
2.0 |
45 |
257 |
63 |
338 |
| 1.2 |
2.0 |
63 |
297 |
88 |
390 |
| 1.5 |
3.0 |
153 |
579 |
214 |
761 |
| 1.7 |
3.0 |
191 |
639 |
267 |
840 |
| 2.0 |
3.5 |
308 |
875 |
430 |
1150 |
| 2.5 |
4.0 |
663 |
1381 |
925 |
1815 |
| 2.5 |
5.5 |
943 |
2019 |
1317 |
2653 |
| 3.0 |
5.0 |
1050 |
2000 |
1571 |
2709 |
| 3.0 |
6.0 |
1312 |
2488 |
1888 |
3292 |
| 3.3 |
4.5 |
1175 |
1884 |
1640 |
2476 |
| 3.3 |
6.0 |
1675 |
2783 |
2338 |
3652 |
| 3.3 |
6.5 |
1814 |
3015 |
2532 |
3961 |
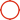
Shunhang Rubber Yokohama Fender


Pressure Compression Test




 Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!  Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail! 


